
The automatic control system of a sesame oil production line integrates multiple hardware and software components to ensure precise, efficient, and stable operation. Central to this system are the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), touchscreen HMI, sensors, and actuators - all working harmoniously to monitor and control critical process parameters.
The PLC acts as the brain of the production line, managing real-time data acquisition and executing control logic based on predefined parameters. The touchscreen HMI offers operators an intuitive interface to monitor status and adjust parameters on-the-fly. High-accuracy sensors continuously measure factors like temperature, flow rate, and pressure, feeding vital inputs back to the PLC. Actuators such as valves and motors respond accordingly, adjusting process conditions to maintain optimal production quality.
Successfully merging hardware with software is paramount to achieving seamless automation. The control logic programmed in the PLC must precisely interpret sensor feedback and generate accurate actuator commands. For example, advanced PID loops regulate temperature within ±2°C tolerance to guarantee oil quality, while flow control loops synchronize extraction rate to meet throughput targets.
Communication protocols such as MODBUS TCP/IP or PROFIBUS ensure robust data exchange between PLCs and HMIs. Software modules are designed modularly to allow quick parameter updates without system downtime. Moreover, embedded diagnostics within the PLC facilitate real-time fault detection and alert operators promptly.
Parameter tuning directly impacts production stability and efficiency. Adjustments focus primarily on thermal control and ingredient flow synchronization. Below is an example of critical PLC parameters and their practical adjustment ranges:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range | Effect on Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Setpoint | Desired oil extraction temperature | 120-130°C | Affects oil yield and flavor |
| PID Gain (Kp) | Proportional gain for temperature control | 1.5 - 3.0 | Stabilizes temperature response |
| Flow Rate Threshold | Minimum sesame seed flow to prevent blockages | 50-70 kg/h | Ensures continuous extraction |
Practically, iterative tuning with monitoring data over multiple production cycles will help pinpoint optimal settings, balancing throughput and quality. Leveraging automated control loops minimizes human errors and improves repeatability.
Despite advanced automation, occasional faults can occur due to sensor drift, actuator wear, or network interruptions. A comprehensive fault diagnosis process involves:
Preventive maintenance schedules, based on manufacturer guidelines and operational hours (e.g., every 2,000 runtime hours), are critical to avoid unexpected downtime. Key tasks include cleaning sensors, inspecting actuator mechanics, firmware updates, and security audits.
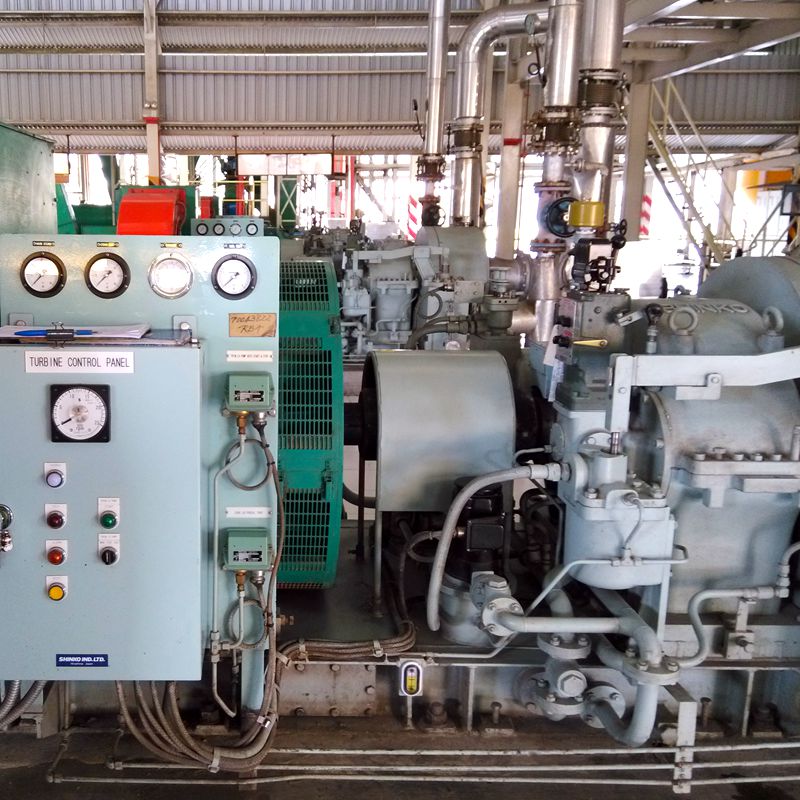
A mid-sized grain processing plant implemented our customized PLC tuning solution and documented notable improvements:
This success stemmed from precise sensor calibration, PID parameter refinement, and operator training via interactive touchscreen tutorials.
Automation needs vary widely based on production capacity and budget. For small enterprises, modular PLC systems paired with scalable HMI interfaces enable cost-effective automated control without excessive complexity. Medium and large plants benefit from integrated solutions featuring:
Tailoring software logic and hardware configuration ensures that each facility achieves an efficient balance of automation sophistication and operational simplicity.

To facilitate rapid learning curves and reduce operator errors, integrating multimedia aids such as step-by-step video tutorials and interactive parameter adjustment demos within the HMI is highly recommended. These resources complement technical manuals, boosting hands-on confidence and adherence to best practices.
Stay informed on the latest PLC firmware upgrades, troubleshooting tips, and custom automation templates by joining our exclusive technical discussion group. Engage in knowledge exchange with peer engineers and receive expert support tailored to your production line.

Download the Complete PDF Operation Manual
Join our technical community now for live Q&A and ongoing updates.

